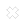
Chickenpox (varicella) infection in pregnancy is relatively uncommon as the majority of mothers have been infected in childhood or have been vaccinated. Once you have had chickenpox, you will be immune from further infection. Chickenpox infection occurs in about three pregnant mothers per 1000 pregnancies.
However, chickenpox in pregnancy can cause complications to both mother and baby. Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called herpes zoster. In adults, it tends to be more serious especially in pregnant mothers.
What are the presenting features of chickenpox?
The features of chickenpox take between 10 to 21 days to appear (incubation period). Usually, one will feel feverish and unwell. This is followed by eruption of itchy watery blisters which can appear anywhere over the body. After about five days, the blisters would burst, crust over and then heal.
How does one get infected with chickenpox?
A person usually gets chickenpox from someone who is presently infected. It is transmitted via respiratory droplets or contact with the blister fluid. A person is contagious two days before the rash appears till all the blisters have crusted over. A person could catch chickenpox by being in close contact with an infected person or being face to face with the infected person for at least five minutes or in the same room with the infected person for at least 15 minutes.
Is shingles the same as chickenpox?
Shingles is caused by the same virus but the features are different. After one has recovered from chickenpox, the virus stays in one’s body (in the nerve root of spinal cord) and they can become active again later if your immune system is impaired. Shingles is a patch of itchy painful blisters on the skin that dry out and crust over in a few days (like a ‘snake’ as the Chinese say).
How effective is the chickenpox vaccination?
The vaccine consists of live weakened virus. The chickenpox vaccination is effective in making nine out of ten women (90 per cent) immune. The immunity can last up to 20 years. In the United States, primary chickenpox infection has fallen by 90 per cent and death rate decreased two-third due to vaccination.
Can a pregnant mother be given the chickenpox vaccination?

You should avoid pregnancy for three months after the injection. The vaccination cannot be given during pregnancy. If you develop a rash after vaccination, you should avoid contact with susceptible persons. However, there has not been any reported case of transmission to the baby or abnormalities of the baby due to the vaccine, for those who conceived after receiving the vaccination.
What if an expectant mother comes into contact with chickenpox?
If you have immunity due to previous infection or vaccination, there is nothing to worry about. If you are not sure, you can have a blood test to find out if you are immune. If you have significant contact during pregnancy and are not immune to chickenpox, you may be given an injection of varicella zoster antibodies (VZIG) up to 10 days after contact with chickenpox and before any rash appears.
VZIG is a human blood product which strengthens the immune system for a short time but does not necessarily prevent chickenpox from developing. VZIG can lessen and shorten the infection. The vaccine does not work once blisters start appearing. However, availability of VZIG is very limited in Malaysia.
What is the treatment for chickenpox during pregnancy?
An antiviral drug, aciclovir can be given within 24 hours (five times a day for one week) of the appearance chickenpox rash. This will reduce the fever and blisters. Aciclovir is only recommended after 20 weeks of pregnancy. There has not been any reported case of baby abnormality with aciclovir. However, there is no medication to prevent your baby from getting chickenpox in the uterus.
What complications can chickenpox cause in pregnancy?

Adults have greater complications compared to childhood infections. The complications include chest infection (pneumonia), inflammation of the liver (hepatitis) and inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). Pneumonia occurs in up to 10 per cent of cases and the severity increased with late gestation. This may be due to the breathing impairment caused by the increasing large womb.
The risk is also greater in smokers and a person with lung disease. Pregnant mothers are five times more likely to succumb to chickenpox infection compared to a non-pregnant adult. However, mortality amongst women caused by these complications is extremely rare.
Should an expectant mother be admitted to the hospital if infected with chickenpox?
Admission to a hospital is advised if the pregnant mother experiences symptoms such as chest and breathing problems, headache, drowsiness, vomiting or feeling sick, vaginal bleeding, severe or bleeding rash. Once admitted, the infected pregnant mum will be isolated from other susceptible patients.
What are the impacts of chickenpox towards the baby during pregnancy and after birth?
The risk of a baby catching chickenpox depends on the stage of pregnancy.
- Up to 28 weeks of pregnancy – There is no evidence of increased risk of early miscarriage. Damage can occur to the eyes, legs, arms, brain, bladder or bowel in one to two of every 100 babies (about one to two percent).
- Between 28 and 36 weeks of pregnancy – The virus stays in the baby’s body but will not cause any symptoms.The virus may become active again causing shingles in the first few years of the child’s life.
- After 36 weeks to birth – The baby may become infected and could be born with chickenpox.
- Around the time of birth – If the baby is born within seven days of your chickenpox rash appearing, the baby may get severe chickenpox. The baby will need to be treated.
- Up to seven days after birth – The baby may get severe chickenpox and will need to be treated. The baby will be monitored for 28 days after you are infected. (Adapted from Patient pamphlet ‘What you need to know – chickenpox in pregnancy – RCOG)
What is the method used to detect chickenpox infection in the unborn baby?
The common detection method is an ultrasound survey of the baby to look for limb deformity, small brain size, swelling of the brain, soft tissue calcification and growth lag. This can only be detected five weeks after the chickenpox infection as the abnormalities are due to shingles infection of the baby.
Should an infected expectant mother deliver her baby earlier than the expected due date?
The timing will depend on the expectant mother’s individual circumstances. It is best to delay delivery until all the blisters have crusted over. This will allow the transfer of immune antibodies to the baby.
How should the baby be delivered?
The choice of the mode of delivery will depend on the expectant mother after consulting with an obstetrician. If a Caesarean section is needed, general anaesthesia may worsen pneumonia infection. An epidural is safer than spinal anaesthesia as the dura (spinal cord covering) is not pierced, preventing the transmission of the chickenpox virus from the skin to the brain.
Can a mother with chickenpox breastfeed her baby?
It is safe to breastfeed if you have or have had chickenpox during pregnancy.
What if another family member has chickenpox at the time the newborn baby is brought home?
If the mother is immune, the baby will be protected by the mother’s immunity and there is nothing to worry about. But if the mother is not immune, then the baby may be given VZIG.